
The study included newborns that attended at least one appointment in each of the three periods: Period I, up to 3 months of corrected age (CA) Period II, 4–6 months of CA and Period III, 7–12 months of CA. Study of preterm very low birth weight newborns followed from 2006 to 2013 in a public institutional hospital program.
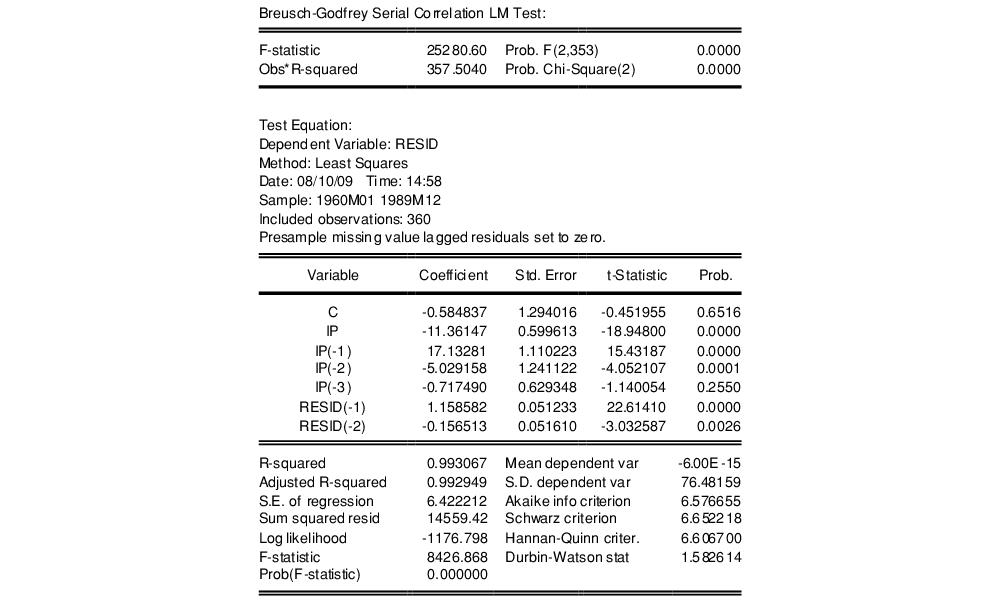
We then write Var(ui | Xi = x) = σ2i ∀ i = 1, …, n.To determine risk factors during neonatal hospital stay and follow-up associated with failure to thrive in the first year of life of very low birth weight newborns. If instead there is dependence of the conditional variance of uiui on XiXi, the error term is said to be heteroskedastic. Which is the error term of heteroskedasticity? In general, the idea of the F -test is to compare the fit of different models. We will not focus on the details of the underlying theory. linearHypothesis () computes a test statistic that follows an F -distribution under the null hypothesis. We test by comparing the tests’ p -values to the significance level of 5%.
#Tests for homoscedasticity in xlstat how to#
How to test for heteroskedasticity in econometrics? Once you fit a regression line to a set of data, you can then create a scatterplot that shows the fitted values of the model vs. The simplest way to detect heteroscedasticity is with a fitted value vs. Which is the best way to detect heteroscedasticity? To satisfy the regression assumptions and be able to trust the results, the residuals should have a constant variance. Heteroscedasticity is a problem because ordinary least squares (OLS) regression assumes that all residuals are drawn from a population that has a constant variance (homoscedasticity). Why is heteroscedasticity a problem in OLS regression? The impact of violating the assumption of homoscedasticity is a matter of degree, increasing as heteroscedasticity increases. Heteroscedasticity (the violation of homoscedasticity) is present when the size of the error term differs across values of an independent variable. What happens when homoscedasticity is violated? Why do we need homoscedasticity?īreusch-Pagan & White heteroscedasticity tests let you check if the residuals of a regression have changing variance. It is a χ2 test.Ī simple method to detect multicollinearity in a model is by using something called the variance inflation factor or the VIF for each predicting variable. It tests whether the variance of the errors from a regression is dependent on the values of the independent variables. What is the test for heteroskedasticity?īreusch Pagan Test It is used to test for heteroskedasticity in a linear regression model and assumes that the error terms are normally distributed. Uneven variances in samples result in biased and skewed test results. This is an important assumption of parametric statistical tests because they are sensitive to any dissimilarities. Homoscedasticity, or homogeneity of variances, is an assumption of equal or similar variances in different groups being compared. What Is Heteroskedasticity? In statistics, heteroskedasticity (or heteroscedasticity) happens when the standard deviations of a predicted variable, monitored over different values of an independent variable or as related to prior time periods, are non-constant. This effect occurs because heteroscedasticity increases the variance of the coefficient estimates but the OLS procedure does not detect this increase. There are two big reasons why you want homoscedasticity: While heteroscedasticity does not cause bias in the coefficient estimates, it does make them less precise. If there is an evident pattern in the plot, then heteroskedasticity is present.ĭo you want heteroskedasticity or homoscedasticity?

Residual Plots One informal way of detecting heteroskedasticity is by creating a residual plot where you plot the least squares residuals against the explanatory variable or ˆy if it’s a multiple regression. How do you test for heteroscedasticity graphically? Residuals can be tested for homoscedasticity using the Breusch–Pagan test, which performs an auxiliary regression of the squared residuals on the independent variables. Oppositely, heteroskedasticity occurs when the variance of the error term is not constant. Homoskedasticity occurs when the variance of the error term in a regression model is constant. What is difference between homoscedasticity and heteroscedasticity?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
